Olive oil is a vegan-friendly product derived from pressed olives. It fits perfectly within a vegan diet.
Olive oil, a staple in Mediterranean cuisine, is celebrated for its numerous health benefits and culinary versatility. Extracted through mechanical means, it contains no animal products or byproducts, making it a plant-based choice suitable for vegans. Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, it’s a heart-healthy option that can enhance the flavor of vegan dishes.
It can be used in cooking, baking, and as a dressing, adding a depth of flavor to plant-based meals. Embracing olive oil within a vegan lifestyle contributes to a balanced diet while ensuring that no animals are harmed or utilized in its production.
Credit: twitter.com
The Essence Of Veganism
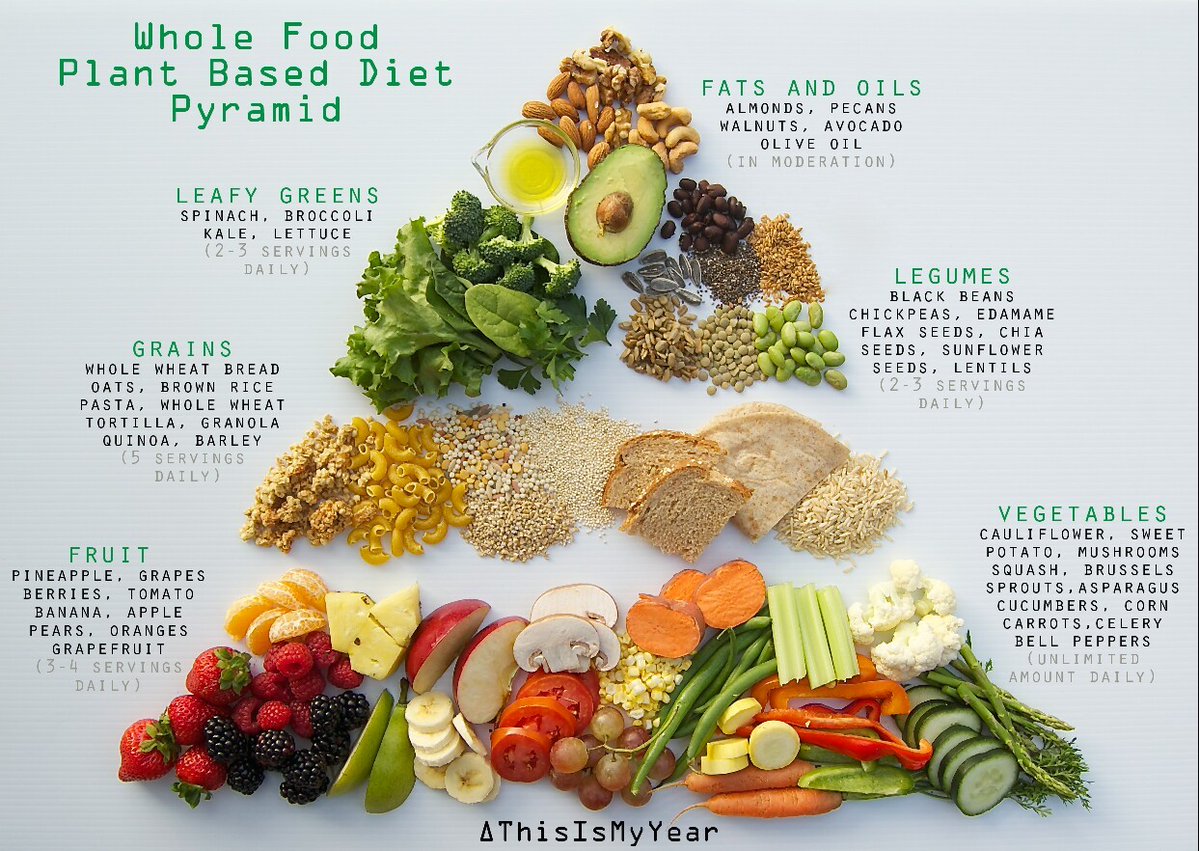
The essence of veganism lies beyond just a diet; it’s a lifestyle choice that reflects a commitment to animal welfare and environmental sustainability. At its core, veganism embraces a plant-based diet, excluding all forms of animal exploitation for food, clothing, or any other purpose. This philosophy extends to all aspects of life, guiding not only what vegans eat but how they interact with the world around them.
The Core Principles And Dietary Restrictions
Veganism is grounded in respect for all living beings. Vegans choose foods that cause no harm to animals. This means no meat, dairy, eggs, or honey. Plant-based alternatives replace traditional animal products. Vegans read labels carefully to avoid hidden animal ingredients.
- No meat, poultry, or fish: Vegans eat beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh instead.
- No dairy: Plant milks, such as almond, soy, and oat, are popular among vegans.
- No eggs: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and commercial egg replacers are used in baking.
- No honey: Vegans sweeten their food with maple syrup, agave nectar, or date syrup.
The Impact Of Food Choices On Veganism
Vegans know that every food choice can make a difference. Eating plant-based helps save animals, conserve water, and reduce carbon emissions. Olive oil is a staple in vegan cooking, as it is plant-derived and does not involve animal harm. It adds flavor and richness to vegan dishes.
| Food Choice | Impact on Animals | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Olive Oil | No direct harm to animals | Low water usage compared to animal products |
| Plant Milks | No animal exploitation | Less greenhouse gas emissions than dairy milk |
| Legumes | Animal-friendly protein source | Improves soil health; lower carbon footprint |

Credit: www.feedyourimmunity.com
Olive Oil Origins
The story of olive oil begins with its roots deeply embedded in history, tracing back to ancient civilizations that first discovered the liquid gold hidden within the humble olive. Olive oil’s rich narrative is intertwined with culture, tradition, and a dedication to craftsmanship that spans thousands of years. As a key component of the vegan diet, olive oil offers a blend of flavor and nutrition that is both timeless and essential.
From Tree To Table: The Production Process
The journey of olive oil from tree to table is a fascinating process of transformation. The life of olive oil starts in sun-kissed groves where olives are carefully grown until they reach perfect ripeness. Once harvested, the olives undergo a meticulous method of pressing and extraction. This process ensures that the oil retains its flavor, aroma, and nutritional properties.
- Olives are picked from trees, either by hand or using modern machinery.
- The fruits are then washed to remove impurities.
- Next comes the crushing, where olives turn into a paste.
- Through pressing or centrifugation, the oil is separated from the paste.
- Finally, the oil is stored in optimal conditions before bottling.
Types Of Olive Oil And Their Characteristics
Different types of olive oil offer unique flavors and benefits. Understanding these varieties is key to selecting the perfect oil for your vegan dishes.
| Type of Olive Oil | Characteristics | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil | High-quality, unrefined, rich in flavor | Dressings, dips, finishing dishes |
| Virgin Olive Oil | Slightly lower quality, good flavor | Cooking, sautéing |
| Pure Olive Oil | Refined, milder taste | Frying, baking |
| Light Olive Oil | Very refined, light in flavor | High-heat cooking |
Nutritional Profile Of Olive Oil
Exploring the nutritional profile of olive oil uncovers why it’s a staple in vegan diets. Rich in essential nutrients, olive oil is not just a simple condiment but a powerhouse of health benefits. Let’s delve into its key components and how they contribute to overall well-being.
Key Components And Health Benefits
Olive oil is packed with monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid. These fats are heart-friendly. They help to maintain healthy cholesterol levels. The oil also contains antioxidants such as vitamin E and polyphenols. Antioxidants protect our cells from damage. Olive oil’s anti-inflammatory properties are linked to the compound oleocanthal. This compound also contributes to its unique flavor.
- High in monounsaturated fats
- Rich in antioxidants like vitamin E and polyphenols
- Contains anti-inflammatory oleocanthal
- Free from sodium and sugar
- Zero cholesterol
Olive oil’s nutrients support heart health and may lower the risk of chronic diseases. Regular consumption can lead to better skin and hair health. It also aids in weight management.
Comparative Analysis With Other Oils
When compared to other oils, olive oil stands out for its health benefits. Unlike coconut oil, it has less saturated fat. This makes it a heart-healthier choice. Olive oil’s smoke point is higher than that of flaxseed oil, which means it’s more stable for cooking at moderate temperatures.
| Olive Oil | Coconut Oil | Flaxseed Oil |
|---|---|---|
| Low in saturated fat | High in saturated fat | Low heat stability |
| High monounsaturated fat | Medium monounsaturated fat | High in omega-3 fatty acids |
| Moderate smoke point | High smoke point | Low smoke point |
Compared to vegetable oils like canola, olive oil is less processed. This means it retains more of its natural nutrients. Olive oil’s unique composition makes it an excellent addition to a vegan diet.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are crucial when discussing whether olive oil fits into a vegan diet. This section explores the impact of olive oil production from both agricultural and animal rights perspectives.
Agricultural Practices And Sustainability
Olive farming has deep roots in Mediterranean cultures, known for its long-standing traditions. Yet, the sustainability of these practices is vital for ethical vegan considerations. Key points include:
- Water usage – Olives require less water compared to other crops, making it a more sustainable option in arid regions.
- Chemical use – The trend towards organic farming reduces harmful chemicals, promoting healthier ecosystems.
- Soil health – Olive trees help in maintaining soil integrity and preventing erosion.
These practices ensure that the environmental impact is minimized, aligning with the ethical standards many vegans uphold.
Animal Rights And Olive Farming
Animal welfare is a core component of vegan ethics. Olive farming’s impact on animals includes:
- Habitat disruption – Farming can lead to habitat loss but is minimal with proper management.
- Pesticides – Organic farming practices help protect local wildlife from harmful pesticides.
Ensuring minimal harm to animal life supports the vegan principle of avoiding animal exploitation.
Olive Oil In Vegan Cooking
Olive oil is a staple in vegan kitchens. Its versatility enhances flavors and adds richness to plant-based dishes. Chefs and home cooks alike treasure it for its health benefits and culinary prowess. Extra virgin olive oil, with its pure extraction process, stands out for its nutritional qualities and robust taste.
Culinary Uses And Vegan Recipes
Olive oil serves multiple roles in vegan cooking. It can be used for sautéing, dressing salads, and baking. It adds depth to soups and stews. It also works as a butter substitute in many recipes.
- Sautéed Vegetables: Olive oil brings out the natural flavors of vegetables.
- Salad Dressing: Mix with vinegar for a simple and healthy dressing.
- Vegan Baking: Use in place of butter for moist cakes and cookies.
Try these vegan recipes with olive oil:
- Olive Oil Roasted Brussels Sprouts
- Chickpea Mediterranean Salad with an olive oil dressing
- Chocolate Olive Oil Cake for a rich, dairy-free dessert
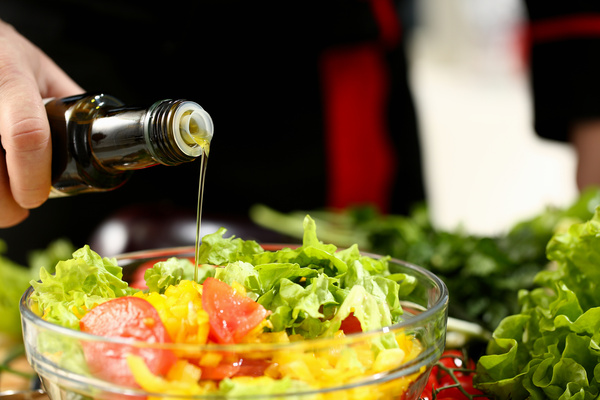
Substitutes And Alternatives
In some recipes, you might want to explore other options. Whether for health, taste, or availability, alternatives to olive oil are plentiful. Consider your dish’s needs when choosing a substitute.
| Substitute | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Coconut Oil | Great for baking and adds a tropical flavor. |
| Avocado Oil | High smoke point, perfect for frying and grilling. |
| Applesauce | For low-fat baking. Keeps baked goods moist. |
Each alternative offers unique properties. Coconut oil brings a hint of sweetness. Avocado oil suits high-heat cooking. Applesauce reduces fat while preserving moisture in baked goods.

Credit: www.oliveoilsfromspain.org
Debunking Myths Around Olive Oil
Olive oil is a staple in many kitchens, praised for its health benefits and flavor. But what about its place in a vegan diet? Let’s dive into the myths and facts to clear up any confusion.
Common Misconceptions
- Olive oil contains animal products: This is false. Olive oil is plant-based, coming from pressed olives.
- It’s processed with animal substances: Another myth. Olive oil production does not involve animal derivatives.
- Vegans can’t consume fats or oils: Incorrect. Vegans can enjoy plant-derived fats like olive oil.
Scientific Evidence And Expert Opinions
Experts agree that olive oil is 100% vegan-friendly. Research shows its benefits for heart health. It’s a great choice for vegans looking for healthy fats.
Label Reading And Certification
Choosing the right olive oil is vital for a vegan diet. The ‘Label Reading and Certification’ process ensures this. Let’s explore how to read labels and find vegan certifications for olive oil.
Understanding Vegan Labels
Labels tell us what’s inside. For vegans, certain labels are crucial. Look for these marks:
- Vegan Society Logo: Confirms no animal products.
- Certified Vegan Logo: No ingredients of animal origin.
- Non-GMO Project Verified: Ensures natural ingredients.
These symbols mean the product is safe for vegans.
Ensuring Olive Oil Is Vegan-friendly
To be sure olive oil is vegan, check these points:
- Read the ingredient list. It should only list olives.
- Look for vegan certification marks on the label.
- Check for cross-contamination warnings.
This approach helps maintain a vegan diet without worry.
Incorporating Olive Oil Into A Vegan Lifestyle
Embracing a vegan lifestyle involves thoughtful choices in diet. Olive oil stands out as a versatile, healthy fat that enhances vegan cooking. It brings flavor and richness to plant-based dishes. Olive oil is a pure juice from olives, making it 100% vegan-friendly.
Daily Consumption Recommendations
How much olive oil should you use daily? The answer varies based on individual dietary needs. Nutritionists often suggest one to two tablespoons for a balanced diet. This portion provides enough healthy fats without excess calories. Consider the following:
- Use olive oil in cooking or as a dressing.
- Remember to account for all oil sources in your diet.
- Adjust amounts based on your total energy intake.
Balancing Diet And Ethics
Vegans value ethics along with health. Olive oil production can be sustainable and ethical. Choose brands that prioritize:
| Criteria | Importance |
|---|---|
| Eco-friendly farming | Reduces environmental impact |
| Fair labor practices | Ensures workers’ rights |
| Animal welfare | Prevents harm to wildlife |
Selecting the right olive oil makes your vegan diet both healthy and responsible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Eat Olive Oil On A Vegan Diet?
Yes, olive oil is suitable for a vegan diet as it is a plant-based fat extracted from olives and contains no animal products.
What Oil Can Vegans Eat?
Vegans can consume a variety of plant-based oils, such as olive, coconut, avocado, sunflower, and canola oils. These oils are derived from vegan-friendly sources and are widely available.
What Do Vegans Use Instead Of Olive Oil?
Vegans often opt for coconut, avocado, or canola oils as alternatives to olive oil. These options provide similar cooking properties and health benefits.
Is Any Oil Not Vegan?
Yes, some oils are not vegan if they involve animal products or by-products, such as fish oil or certain emulsified oils containing egg yolk.
Conclusion
To sum up, olive oil is indeed a staple for those on a vegan diet. It’s plant-based, packed with nutrients, and versatile in cooking. Embracing this heart-healthy oil can enhance your meals while keeping your diet animal-free. For vegans seeking flavor and health, olive oil is a clear winner.

